
In this article we will discuss the meaning of the isosceles triangle, its properties and formula and if you solved examples. Therefore, the given triangle is an obtuse angled triangle. Since, the measure of one of the angles of the triangle is greater than 90°. The measure of the third angle of the given triangle comes out to be 120°. If in an isosceles triangle, each of the base angles is 40°, then the triangle is: The triangle is an equilateral triangle.ĥ. So, each interior angle of a given triangle is 60°, which means each side of the triangle is equal (the sides opposite to equal angles are equal). The measure of the third angle of the given triangle comes out to be 60°. If two angles of a triangle are 60° each, then the triangle is:īy interior angle sum property of triangle, In the right angled isosceles triangle, the center of the circumcircle lies on the hypotenuse and the radius of the circumcircle is half the length of the hypotenuse.Īn isosceles triangle whose two equal sides length is ‘a’ unit and length of its base is ’b’ unit. In the right angled isosceles triangle, the altitude on the hypotenuse is half the length of the hypotenuse. In the right angled isosceles triangle, one angle is a right angle (90 degrees) and the other two angles are both 45 degrees. Two isosceles triangles are always similar. The medians drawn from vertex B and vertex C will not bisect the opposite sides AB and AC. The median drawn from vertex A will bisect BC at right angles.

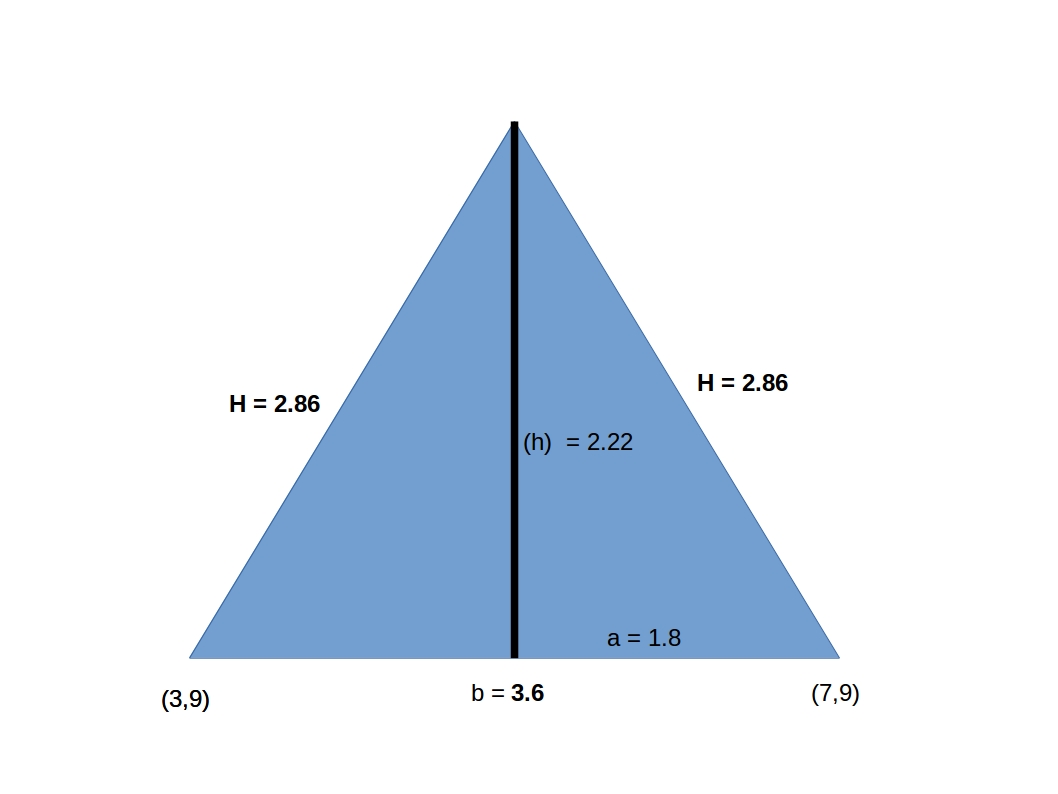
In the above figure, triangle ADB and triangle ADC are congruent right-angled triangles. The altitude from the vertex divides an isosceles triangle into two congruent right-angled triangles. The altitude from vertex A to the base BC is the angle bisector of the vertex angle ∠ A. The altitude from vertex A to the base BC is the perpendicular bisector of the base BC. In the above figure, ∠ B and ∠C are of equal measure. The angles opposite to equal sides are equal in measure. In the above figure, sides AB and AC are of equal length ‘a’ unit. Now, we will discuss the properties of an isosceles triangle.Īn Isosceles Triangle has the Following Properties:

Obtuse angled triangle: A triangle whose one interior angle is more than 90 0.
Right angled triangle: A triangle whose one interior angle is 90 0. Scalene triangle: A triangle whose all three sides are unequal.Ĭlassification of Triangles on the Basis of their Angles is as FollowsĪcute angled triangle: A triangle whose all interior angles are less than 90 0. Isosceles triangle: A triangle whose two sides are equal. Each of them has their own individual properties.Ĭlassification of Triangles on the Basis of their Sides is as Follows:Įquilateral triangle: A triangle whose all the three sides are equal. Triangles are classified into different types on the basis of their sides and angles.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
